What Is Bitcoin Halving and How Does It Affect the Price?
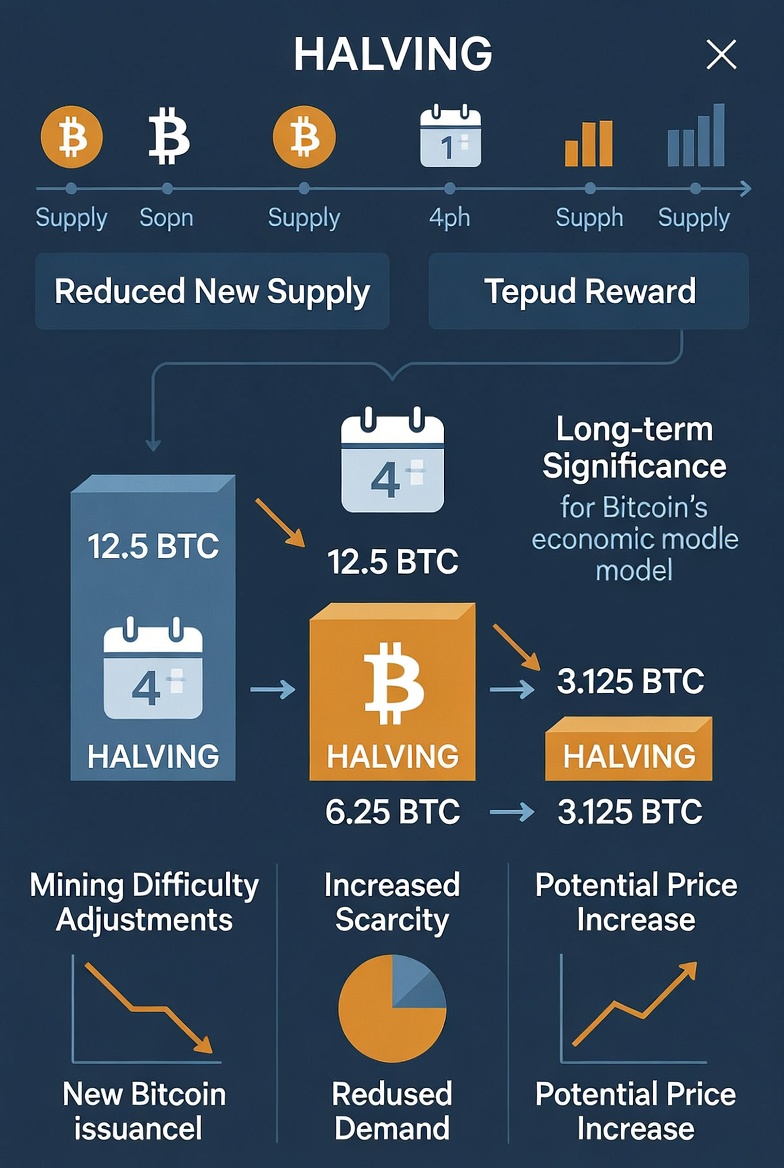
Bitcoin halving is a major event in the Bitcoin network that reduces the reward given to miners by half. It happens approximately every four years and is built into Bitcoin’s code from the beginning. The purpose of halving is to control inflation and ensure that Bitcoin’s total supply remains limited to 21 million coins.
To understand halving, you first need to understand how Bitcoin is created. New bitcoins enter circulation through mining. Miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems, and when they successfully add a new block to the blockchain, they receive a block reward in Bitcoin. This reward is the main way new bitcoins are introduced into the system.
When Bitcoin was launched in 2009, the block reward was 50 BTC per block. After the first halving in 2012, the reward dropped to 25 BTC. In 2016, it was reduced to 12.5 BTC. In 2020, it became 6.25 BTC. In 2024, the most recent halving reduced the reward further to 3.125 BTC per block. This process will continue until all 21 million bitcoins are mined, which is expected to happen around the year 2140.
The main purpose of Bitcoin halving is to reduce the rate at which new bitcoins are created. By cutting the supply growth in half, Bitcoin becomes more scarce over time. Scarcity is one of the key factors that can influence price.
How Halving Affects Bitcoin’s Price
Halving directly reduces the supply of new bitcoins entering the market. If demand remains the same or increases while new supply decreases, basic economic principles suggest that the price may rise. This is why many investors pay close attention to halving events.
Historically, previous halving events have been followed by significant price increases over the next 12 to 18 months. After the 2012 halving, Bitcoin experienced a major bull run in 2013. After the 2016 halving, the price increased dramatically in 2017. Following the 2020 halving, Bitcoin reached new all-time highs in 2021. However, it is important to understand that past performance does not guarantee future results.
There are several reasons why halving can impact price:
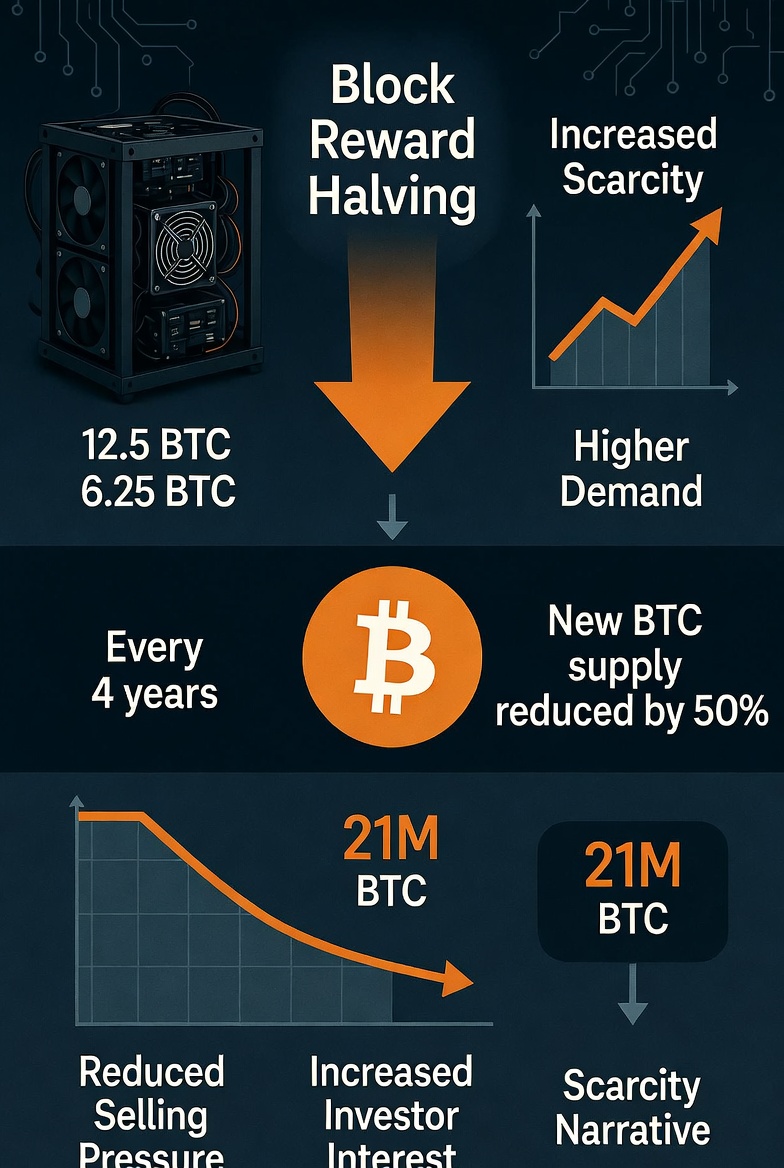
Reduced Selling Pressure
Miners often sell part of their Bitcoin rewards to cover electricity and operational costs. When the block reward is cut in half, miners receive fewer bitcoins, which may reduce the amount they sell in the market. Lower selling pressure can contribute to price growth.
Increased Investor Interest
Halving events attract attention from media, analysts, and investors. This increased awareness can bring new buyers into the market, increasing demand.
Scarcity Narrative
Bitcoin is often compared to digital gold because of its limited supply. Halving strengthens this scarcity narrative. As fewer new coins are created, Bitcoin becomes harder to obtain, which can increase its perceived value.
Impact on Miners
While halving can be positive for price in the long term, it creates challenges for miners. Since their rewards are cut in half, their revenue immediately drops unless the Bitcoin price increases. This can force less efficient miners to shut down operations if they cannot cover costs.
After a halving, the network’s mining difficulty may adjust as some miners leave. Over time, only the most efficient and well-equipped mining operations remain profitable.
Does Price Always Go Up After Halving?
It is a common belief that Bitcoin’s price always rises after halving, but this is not guaranteed. The market is influenced by many factors, including global economic conditions, government regulations, investor sentiment, institutional adoption, and overall demand for cryptocurrency.
Sometimes, the price may rise before the halving because investors expect future growth. In other cases, the market may experience short-term volatility immediately after the event.
Long-Term Significance of Halving
Bitcoin halving plays a crucial role in maintaining its economic model. Unlike traditional currencies, which can be printed in unlimited amounts by central banks, Bitcoin has a predictable and transparent supply schedule. This controlled supply is one of the main reasons many investors see Bitcoin as a hedge against inflation.
As the block reward continues to decrease over time, transaction fees are expected to become a more important source of income for miners. Eventually, when all bitcoins are mined, miners will rely primarily on transaction fees to secure the network.
Conclusion
Bitcoin halving is a built-in mechanism that reduces mining rewards by 50 percent approximately every four years. It slows down the creation of new bitcoins and increases scarcity. Historically, halving events have been followed by major price increases, but future results are never guaranteed. While halving reduces supply and can create upward price pressure, many other market factors also influence Bitcoin’s value. For investors and beginners, understanding halving is essential to understanding how Bitcoin’s economic system works.