How Bitcoin Mining Works – Step-by-Step Guide
Bitcoin mining is the process through which new bitcoins are created and transactions are verified on the network. It is a fundamental part of how Bitcoin operates without a central authority. Mining ensures that transactions are secure, verified, and permanently recorded on the blockchain.
To understand Bitcoin mining, you first need to understand that Bitcoin runs on a decentralized network. There is no central bank or company controlling it. Instead, thousands of computers around the world work together to maintain the system. These computers are called miners.
Step 1: Bitcoin Transactions Are Created
When someone sends Bitcoin to another person, a transaction is created. This transaction includes information such as the sender’s wallet address, the receiver’s wallet address, and the amount of Bitcoin being sent. This transaction is broadcast to the Bitcoin network and waits to be verified.
Step 2: Transactions Are Collected into Blocks
Miners collect these pending transactions and group them into a block. A block is simply a list of recent Bitcoin transactions waiting to be confirmed. Each block also contains a reference to the previous block, which links them together in a chain. This chain of blocks is called the blockchain.
Step 3: Solving a Mathematical Problem
Before a block can be added to the blockchain, miners must solve a complex mathematical puzzle. This process is known as Proof of Work. The puzzle requires significant computational power. Miners use specialized hardware called ASIC miners to perform trillions of calculations per second in order to find the correct solution.
The goal is to find a special number called a hash that meets specific conditions set by the network. The first miner to find the correct hash wins the right to add the block to the blockchain.
Step 4: Block Verification and Addition
Once a miner finds the correct solution, the new block is shared with the rest of the network. Other nodes verify that the solution is correct and that all transactions in the block are valid. If everything checks out, the block is added to the blockchain permanently.
Step 5: Mining Rewards
As a reward for solving the puzzle and securing the network, the miner receives newly created Bitcoin. This is called the block reward. In addition to the block reward, miners also earn transaction fees paid by users who want their transactions processed quickly.
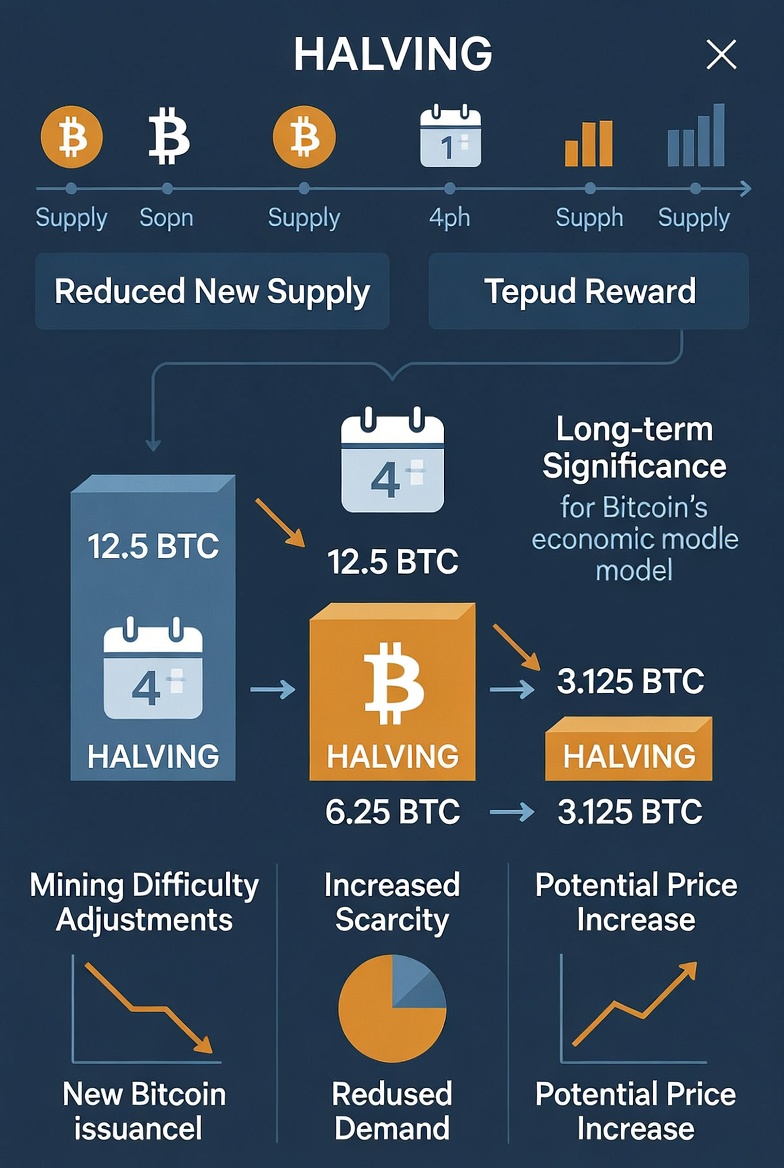
The block reward is not fixed forever. Approximately every four years, a process called halving reduces the reward by half. This event is known as Bitcoin Halving. It ensures that Bitcoin’s total supply remains limited to 21 million coins.
Why Mining Is Important
Bitcoin mining serves two main purposes. First, it introduces new bitcoins into circulation. Second, it secures the network by verifying transactions and preventing double spending. Double spending means trying to use the same Bitcoin twice, which mining helps prevent through verification and consensus.

Hardware Used in Mining
In the early days of Bitcoin, mining could be done using a normal computer CPU. As competition increased, miners started using GPUs, which are more powerful. Today, most serious miners use ASIC machines (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits). These devices are specifically designed for mining Bitcoin and are much more efficient than regular computers.
Energy Consumption
Bitcoin mining requires a large amount of electricity because of the computational power needed to solve cryptographic puzzles. This has led to discussions about environmental impact. Some mining operations are now using renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydro power to reduce their carbon footprint.
Mining Difficulty
The Bitcoin network automatically adjusts the difficulty of the mathematical puzzle approximately every two weeks. If more miners join the network, the difficulty increases. If miners leave, the difficulty decreases. This adjustment ensures that a new block is added roughly every 10 minutes.
Mining Pools
Because mining has become highly competitive, individual miners often join mining pools. A mining pool is a group of miners who combine their computing power to increase their chances of solving a block. When the pool successfully mines a block, the reward is shared among members based on their contribution.
Is Bitcoin Mining Profitable in 2026?
Mining profitability depends on several factors, including electricity costs, hardware efficiency, Bitcoin price, and mining difficulty. In regions with cheap electricity and access to modern ASIC machines, mining can still be profitable. However, for beginners without significant investment, it can be challenging to compete with large-scale mining farms.
Risks of Mining
Mining requires a high initial investment in hardware and infrastructure. Equipment can become outdated quickly as technology improves. Bitcoin price volatility can also affect profitability. If the price drops significantly, miners may struggle to cover electricity and operational costs.
Conclusion
Bitcoin mining is the backbone of the Bitcoin network. It verifies transactions, secures the system, and introduces new coins into circulation. The process involves collecting transactions, solving complex mathematical problems, adding blocks to the blockchain, and earning rewards. While mining can be profitable, it requires technical knowledge, powerful hardware, and careful planning. For beginners, understanding how mining works is essential before deciding to participate in this competitive industry.